Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2023; 20(5):595-605. doi:10.7150/ijms.80563 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Farnesoid X receptor is inhibited after ileum transposition in diabetic rats: its hypoglycemic effect
Department of General Surgery, Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Shuaifuyuan 1#, Beijing 100730, P. R. China
Abstract
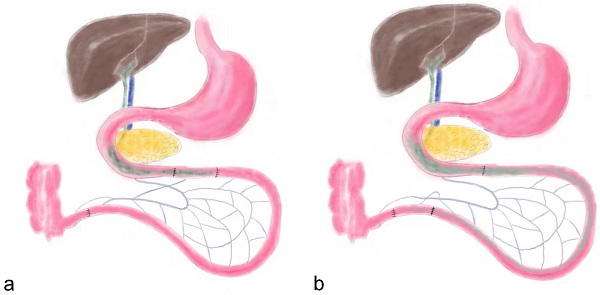
Background: Aim to investigate bile acid profile changes and the Farnesoid X receptor (FXR) status after ileotransposition (IT), and reveal its possible hypoglycemic mechanism.
Methods: Twenty male diabetic rats were randomly assigned into the IT group and the sham IT (SH) group. Bile acid profiles were measured using an ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Glucose metabolism was monitored after oral administration of FXR inhibitor and agonist. And the expression of key FXR target genes were measured.
Results: The levels of β-muricholic acid (P = 0.047), tauro-α-muricholic acid and tauro-β-muricholic acid (P < 0.001) in plasma in the IT group were higher than those in the SH group, and the levels of taurocholic acid (P = 0.049) and turoursodeoxycholic acid (P = 0.030) were lower than those in the SH group. After inhibition of intestinal FXR, the glucose metabolism in the SH group was improved. When FXR agonist was given, the blood glucose level was increased in both groups. After sacrifice, the levels of glycoursodeoxycholic acid, tauro-α-muricholic acid and tauro-β-muricholic acid in liver and ileum tissues were higher than those in the SH group (P < 0.05), the level of α- muricholic acid (P < 0.001) in liver tissues were lower than that in the SH group. Moreover, the expression of CYP7A1 mRNA (P < 0.001) and FGF15 mRNA (P = 0.001) in the IT group was significantly higher, and the expression of PEPCK mRNA (P = 0.004), SREPB1c mRNA (P = 0.005) and SRB1 mRNA (P = 0.001) were significantly lower than that in the SH group.
Conclusions: We demonstrate a remarkable heterogeneity of BA profiles after IT, FXR activation might has a detrimental effect on glucose metabolism.
Keywords: diabetes mellitus, bile acids and salts, farnesoid X receptor, ileum, glucose

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact