3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2023; 20(3):406-414. doi:10.7150/ijms.79525 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Exogenous Lipoxin A4 attenuates IL4-induced Mucin Expression in Human Airway Epithelial Cells
1. BKPlus21, Department of Microbiology, School of medicine, Konkuk University, Seoul, Korea
2. Departments of Otorhinolaryngology-Head & Neck Surgery, School of medicine, Konkuk University, Seoul, Korea
3. Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Konkuk University Medical Center, Seoul, Korea
Abstract
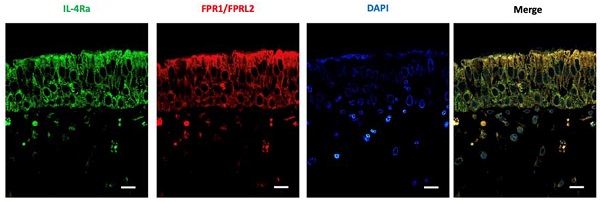
Introduction: The proinflammatory cytokine interleukin-4 (IL-4) induces mucus hypersecretion by human airway epithelial cells and the MAP kinase signalling pathway may be important in terms of IL-4-induced MUC5AC gene expression. Lipoxin A4 (LXA4) is an arachidonic acid-derived mediator that promotes inflammation by binding to the anti-inflammatory receptors (ALXs) or the formyl-peptide receptor like-1 (FPRL1) protein expressed by airway epithelial cells. Here, we explore the effects of LXA4 on IL-4-induced mucin gene expression in, and secretion from, human airway epithelial cells.
Methods: We co-treated cells with IL-4 (20 ng/mL) and LXA4 (1 nM) and measured the expression levels of mRNAs encoding MUC5AC and 5B via real-time polymerase chain reaction; protein expression levels were determined by Western blotting and immunocytofluorescence. The ability of IL-4 and LXA4 to suppress protein expression was determined by Western blotting.
Results: IL-4 increased MUC5AC and 5B gene and protein expression. LXA4 suppressed IL-4-induced MUC5AC and 5B gene and protein expression by interacting with the IL4 receptor and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway, including both phospho-p38 MAPK and phospho-extracellular signal-regulated kinase (phospho-ERK). IL-4 and LXA4 increased and decreased, respectively, the number of cells that stained with anti-MUC5AC and 5B antibodies.
Conclusions: LXA4 may regulate mucus hypersecretion induced by IL4 in human airway epithelial cells.
Keywords: Lipoxin A4, IL-4, MUC5AC, MUC5B, MAPK

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact