3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2023; 20(3):307-317. doi:10.7150/ijms.80942 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Nicotinamide mononucleotides alleviated neurological impairment via anti-neuroinflammation in traumatic brain injury
1. Emergency Center, Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan, China.
2. Department of Biological Repositories, Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan, China.
3. Hubei Clinical Research Center for Emergency and Resuscitation, Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan, China.
# These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
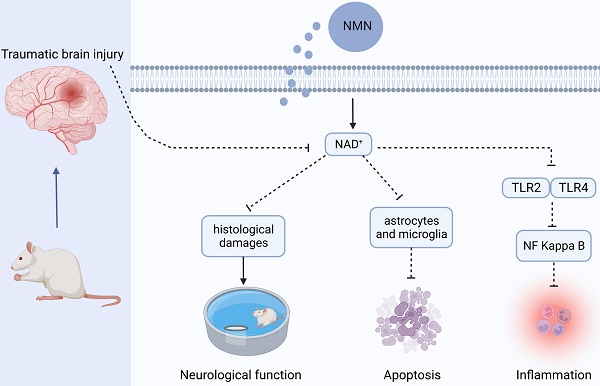
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is one of the main factors of death and disability in adults with a high incidence worldwide. Nervous system injury, as the most common and serious secondary injury after TBI, determines the prognosis of TBI patients. NAD+ has been confirmed to have neuroprotective effects in neurodegenerative diseases, but its role in TBI remains to be explored. In our study, nicotinamide mononucleotides (NMN), a direct precursor of NAD+, was used to explore the specific role of NAD+ in rats with TBI. Our results showed that NMN administration markedly attenuated histological damages, neuronal death, brain edema, and improved neurological and cognitive deficits in TBI rats. Moreover, NMN treatment significantly suppressed activated astrocytes and microglia after TBI, and further inhibited the expressions of inflammatory factor. Besides, RNA sequencing was used to access the differently expressed genes (DEGs) and their enriched (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) KEGG pathways between Sham, TBI, and TBI+NMN. We found that 1589 genes were significantly changed in TBI and 792 genes were reversed by NMN administration. For example, inflammatory factor CCL2, toll like receptors TLR2 and TLR4, proinflammatory cytokines IL-6, IL-11 and IL1rn which were activated after TBI and were decreased by NMN treatment. GO analysis also demonstrated that inflammatory response was the most significant biological process reversed by NMN treatment. Moreover, the reversed DEGs were typically enriched in NF-Kappa B signaling pathway, Jak-STAT signaling pathway and TNF signaling pathway. Taken together, our data showed that NMN alleviated neurological impairment via anti-neuroinflammation in traumatic brain injury and the mechanisms may involve TLR2/4-NF-κB signaling.
Keywords: Traumatic brain injury, Nicotinamide mononucleotides, anti-neuroinflammation, neuronal injury, NF-kappa B

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact