3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2023; 20(3):287-291. doi:10.7150/ijms.79830 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Robot-assisted versus conventional laparoscopic radical hysterectomy in cervical cancer stage IB1
1. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, St. Vincent's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Republic of Korea
2. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Daejeon St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Republic of Korea
3. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Republic of Korea
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study was to compare survival outcomes of robot-assisted laparoscopic radical hysterectomy (RRH) and conventional laparoscopic radical hysterectomy (LRH) in cervical cancer stage IB1.
Method: This is a retrospective study of patients with cervical cancer stage IB1 who surgically treated by either RRH or LRH. Oncologic outcomes of the patients were compared according to surgical approach.
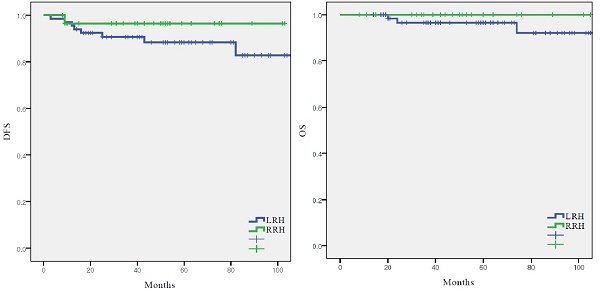
Results: In total, 66 and 29 patients were assigned to LRH and RRH groups. All patients had stage IB1 disease (FIGO 2018). Intermediate risk factors (tumor size, LVSI, and deep stromal invasion), proportion of patients receiving adjuvant therapy (30.3% vs. 13.8%, p = 0.09), and median follow-up time (LRH, 61 months; RRH, 50 months; p=0.085) did not differ significantly between the two groups. The recurrence rate was higher in the LRH group; however, there was no significant difference between the two groups (p=0.250). DFS (55.4 vs 48.2 months, p = 0.250), and OS (61.2 vs 50.0 months, p = 0.287) were similar between the LRH and RRH groups.
Conclusion: In patients with a tumor size < 2 cm, the recurrence rate was lower in RRH group; however, there was no significant difference. Further large-scale RCTs and clinical studies are required to provide relevant data.
Keywords: cervical cancer, robot surgery, robot-assisted laparoscopic radical hysterectomy, RACC

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact