Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2023; 20(1):11-22. doi:10.7150/ijms.76603 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Meibomian gland dysfunction patients benefit in ocular parameters and tear chemokines after thermal pulsation treatment
1. Department of Ophthalmology and Vision Science, The Eye, Ear, Nose and Throat Hospital of Fudan University, Shanghai 200031, P.R. China
2. NHC Key Laboratory of Myopia, Laboratory of Myopia, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Fudan University, Shanghai 200031, P.R. China
3. Department of Ophthalmology, Huadong Hospital of Fudan University, Shanghai, China
Abstract
Objectives: To investigate the effect of thermal pulsation treatment on meibomian gland function, ocular parameters and tear inflammatory cytokines compared with the warm compress group.
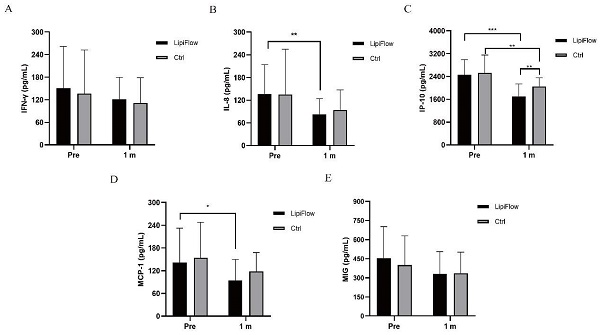
Methods: Twenty-five participants with MGD underwent a 12-minute thermal pulsation treatment, while 25 participants with MGD underwent manual warm compress treatment. MGD related parameters, including meibomian gland function (MGE, MQ and lid margin), tear stability (NIKBUT, FBUT and LLT), tear secretion (SIT, and TMH), were examined and OSDI questionnaire was also obtained. Tear chemokines (MIG, IFN-γ, IL-8, IP-10 and MCP-1) were examined and analyzed the correlations with MGD related parameters and OSDI.
Results: Compared with warm compress subjects, OSDI, lid margin and tear stability were found improved more in thermal pulsation treatment at 3 months (OSDI: *p = 0.014, lid margin: *p = 0.021, LLT: **p = 0.008, CFS: *p = 0.028). The level of IP-10 and MIG decreased more in thermal pulsation group than in warm compress group (IP-10: *p = 0.021, MIG: *p = 0.039). IP-10 was positively correlated with MQ (r = 0.522, *p = 0.037) and negatively correlated with tear stability (r = -0.613, **p = 0.002), and OSDI was only positively correlated with IL-8 (r = 0.679, ***p < 0.001). The decrease of MIG was positively correlated with less corneal epithelium injury (r = 0.557, **p = 0.006) and meibograde (r = 0.49, *p = 0.019).
Conclusions: Thermal pulsation treatment obviously improved MGD probably by attenuating tear CXCL chemokines in ocular surface of MGD patients, which demonstrated an efficacy and well-tolerated therapy in clinical.
Keywords: meibomian gland dysfunction, thermal pulsation treatment, tear chemokines, CXCL cytokines, tear film stability

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact