3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2022; 19(10):1510-1518. doi:10.7150/ijms.76077 This issue Cite
Research Paper
EGF Contributes to Hypertrophy of Human Ligamentum Flavum via the TGF-β1/Smad3 Signaling Pathway
1. Division of Spine Surgery, Department of Orthopaedics, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China
2. The First School of Clinical Medicine, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China
3. Department of Radiation Oncology, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China
4. Department of Orthopedics, The Third Affiliated Hospital, Southern Medical University, Academy of Orthopedics, Guangzhou, China
Abstract
Background: The most common spinal disorder in elderly is lumbar spinal canal stenosis (LSCS). Previous studies showed that ligamentum flavum hypertrophy (LFH) with fibrosis as the main pathological change is one of the pathogenic factors leading to LSCS. Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF) is known to have an intimate relationship with fibrosis in various tissues. Nevertheless, currently, there are few studies regarding EGF in LFH. The effect of EGF on the development of LFH is unknown, and the underlying pathomechanism remains unclear. In this study, we investigated the role of EGF in LFH and its potential molecular mechanism.
Methods: First, the expression levels of EGF, phosphorylation of EGF receptor (pEGFR), Transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1), Phosphorylated Smad3 (pSmad3), collagen I and collagen III were examined via immunohistochemistry and Western blot in LF tissues from patients with LSCS or Non-LSCS. Second, primary LF cells were isolated from adults with normal LF thickness and were cultured with different concentrations of exogenous EGF with or without erlotinib/TGF-β1-neutralizing antibody.
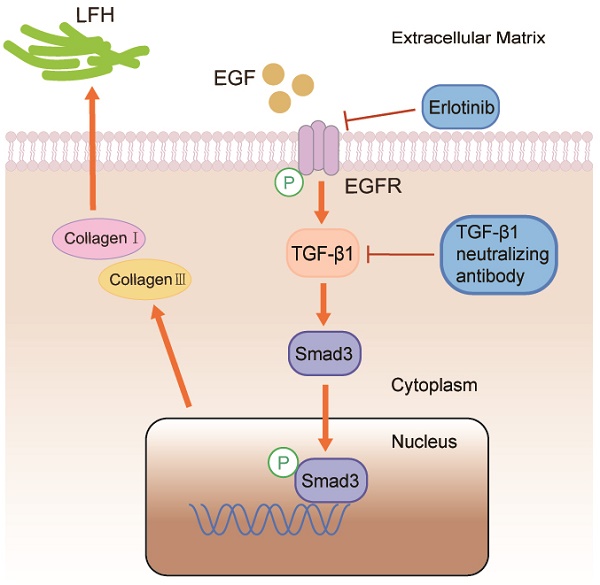
Results: The results showed that EGF, pEGFR, TGF-β1, pSmad3, collagen I and collagen III protein expression in the LSCS group was significantly higher than that in the Non-LSCS group. Meanwhile, pEGFR, TGF-β1, pSmad3, collagen I and collagen III protein expression was significantly enhanced in LF cells after exogenous EGF exposure, which can be notably blocked by erlotinib. In addition, pSmad3, collagen I and collagen III protein expression was blocked by TGF-β1-neutralizing antibody.
Conclusions: EGF promotes the synthesis of collagen I and collagen III via the TGF-β1/Smad3 signaling pathway, which eventually contributes to LFH.
Keywords: ligamentum flavum, hypertrophy, EGF, TGF-β1, Smad3

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact