Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2022; 19(7):1093-1102. doi:10.7150/ijms.73077 This issue Cite
Research Paper
[6]-Gingerol induces Caspase-Dependent Apoptosis in Bladder Cancer cells via MAPK and ROS Signaling
1. Division of Longevity and Biofunctional Medicine, Pusan National University School of Korean Medicine, Yangsan 50612, Republic of Korea.
2. Department of Physiology, Dongguk University College of Medicine, Gyeongju, 38066. Republic of Korea.
3. Channelopathy Research Center (CRC), Dongguk University College of Medicine, 32 Dongguk-ro, Ilsan Dong-gu, Goyang, Gyeonggi-do, 10326. Republic of Korea.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
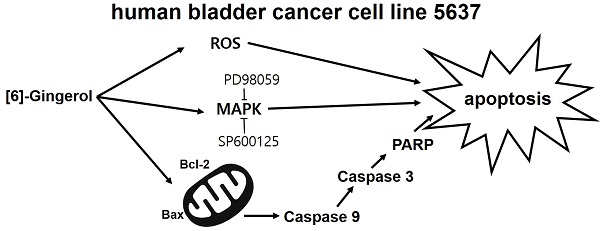
The anti-cancer effects of [6]-gingerol ([6]-GIN), the main active polyphenol of ginger (Zingiber officinale), were investigated in the human bladder cancer cell line 5637. [6]-GIN inhibited cell proliferation, increased sub‑G1 phase ratios, and depolarized mitochondrial membrane potential. [6]-GIN-induced cell death was associated with the downregulation of B‑cell lymphoma 2 (BCL‑2) and survivin and the upregulation of Bcl‑2‑associated X protein (Bax). [6]-GIN activated caspase‑3 and caspase-9 and regulated the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs). Further, [6]-GIN also increased the intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels and TG100-115 or tranilast increased [6]-GIN‑induced cell death. These results suggest that [6]-GIN induced apoptosis in the bladder cancer cell line 5637 and therefore has the potential to be used in the development of new drugs for bladder cancer treatment.
Keywords: [6]-gingerol, cell proliferation, apoptosis, bladder cancer, 5637

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact