3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2022; 19(3):572-587. doi:10.7150/ijms.70445 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Expression Landscape and Functional Roles of HOXA4 and HOXA5 in Lung Adenocarcinoma
1. Department of Pathology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, No.6 Shuangyong Rd, Nanning, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, 530021, P.R. China.
2. Department of Medical Oncology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, No.6 Shuangyong Rd, Nanning, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, 530021, P.R. China.
3. Department of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, No.6 Shuangyong Rd, Nanning, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, 530021, P.R. China.
4. Department of Clinical Laboratory, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University/Nanning Second People's Hospital, No. 13 Dancun Road, Nanning, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, 530031, P. R. China.
5. Department of Pathology, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, No.121 of Jiangjiayuan, Nanjing, Jiangsu Province, 210000, P.R. China.
6. Ward of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Respiratory Medicine, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, No. 6, Shuangyong Road, Nanning, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, 530021, P.R. China.
7. Department of Pathology, Guigang People's Hospital of Guangxi/The Eighth Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, No. 1, Zhongshan Middle Road, Guigang, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, 530021, P.R. China.
Abstract
Background: The role of HOXA family genes in the occurrence and progression of a variety of human cancers has been scatteredly reported. However, there is no systematic study on the differential expression, prognostic significance and potential molecular mechanism of HOXA4 and HOXA5 in LUAD.
Methods: In-house immunohistochemistry (IHC), multi-center microarrays, RT-qPCR and RNA-seq data were incorporated for comprehensively evaluating the expression and prognostic value of HOXA4 and HOXA5 in LUAD. The mechanism of HOXA4 and HOXA5 in the formation and development of LUAD was analyzed from multiple aspects of immune correlations, upstream transcriptional regulation, functional states of single cells and co-expressed gene network. The functional roles of HOXA4 and HOXA5 in LUAD were validated by in vitro experiments.
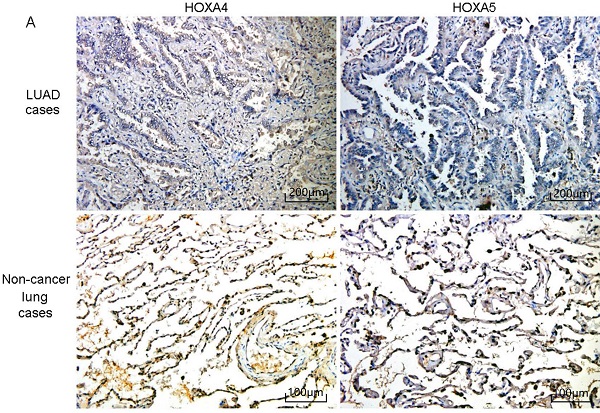
Results: As a result, in 3201 LUAD samples and 2494 non-cancer lung samples, HOXA4 and HOXA5 were significantly downexpressed (P < 0.05). The aberrant expression of HOXA5 was significantly correlated with the clinical progression of LUAD (P < 0.05). HOXA5 showed remarkable prognostic value for LUAD patients (P < 0.05). The expression of HOXA4 and HOXA5 in LUAD were negatively correlated with tumor purity and positively correlated with the infiltration of various immune cells such as B cells, T cells and macrophages. HOXA4 and HOXA5 overexpression had notable inhibitory effect on the proliferation, migration and invasion of LUAD cells.
Conclusions: In conclusion, the identified downexpressed HOXA4 and HOXA5 had significant distinguishing ability for LUAD samples and affected the cellular functions of LUAD cells. The low expression of HOXA5 indicated worse overall survival of LUAD patients. Therefore, the two HOXA family genes especially HOXA5 may serve as potential biomarkers for LUAD.
Keywords: HOXA4 and HOXA5, in vitro experiments, lung adenocarcinoma, microarray, RNA-seq

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact