3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2021; 18(16):3684-3691. doi:10.7150/ijms.64359 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Reconstruction of the orbital floor using supercritical CO2 decellularized porcine bone graft
1. School of Post Baccalaureate Medicine, Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan.
2. Center of Research and Development, ACRO Biomedical Co., Ltd. Kaohsiung, Taiwan.
3. Division of Plastic Surgery, Department of Surgery, Kaohsiung Medical University Hospital, Kaohsiung, Taiwan.
4. Regenerative medicine and cell therapy research center, Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan.
5. Department of Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, College of Medicine, Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan.
6. Department of Surgery, Kaohsiung Municipal Siaogang Hospital, Kaohsiung, Taiwan.
Abstract
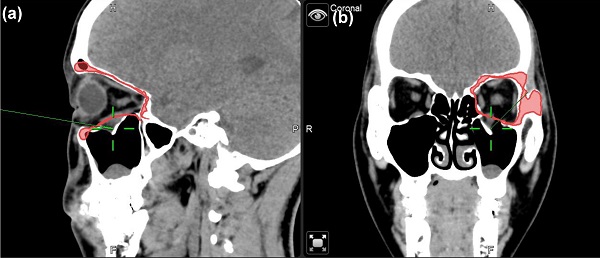
Orbital floor fractures subsequently lead to consequences such as diplopia and enophthalmos. The graft materials used in orbital floor fractures varied from autografts to alloplastic grafts, which possess certain limitations. In the present study, a novel porcine bone matrix decellularized by supercritical CO2 (scCO2), ABCcolla® Collagen Bone Graft, was used for the reconstruction of the orbital framework. The study was approved by the institutional review board (IRB) of Kaohsiung Medical University Chung-Ho Memorial Hospital (KMUH). Ten cases underwent orbital floor reconstruction in KMUH in 2019. The orbital defects were fixed by the implantation of the ABCcolla® Collagen Bone Graft. Nine out of ten cases used 1 piece of customized ABCcolla® Collagen Bone Graft in each defect. The other case used 2 pieces of customized ABCcolla® Collagen Bone Graft in one defect area due to the curved outline of the defect. In the outpatient clinic, all 10 cases showed improvement of enophthalmos on CT (computerized tomography) at week 8 follow-up. No replacement of implants was needed during follow-ups. To conclude, ABCcolla® Collagen Bone Graft proved to be safe and effective in the reconstruction of the orbital floor with high accessibility, high stability, good biocompatibility, low infection rate and low complication rate.
Keywords: orbital wall reconstruction, ABCcolla® collagen bone graft, supercritical carbon dioxide, bone graft, xenogenic graft

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact