3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2021; 18(10):2137-2145. doi:10.7150/ijms.55633 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Oral Resveratrol supplementation attenuates exercise-induced Interleukin-6 but not Oxidative Stress after a high intensity cycling challenge in adults
1. Department of Physical Education, National Taichung University of Education, Taichung City, Taiwan.
2. Department of Nutrition, Institute of Biomedical Nutrition, Hungkuang University, Taichung City, Taiwan.
3. Department of Kinesiology, California State University, Stanislaus, Turlock, CA, USA.
4. Department of Exercise and Health Science, National Taipei University of Nursing and Health Science, Taipei City, Taiwan.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
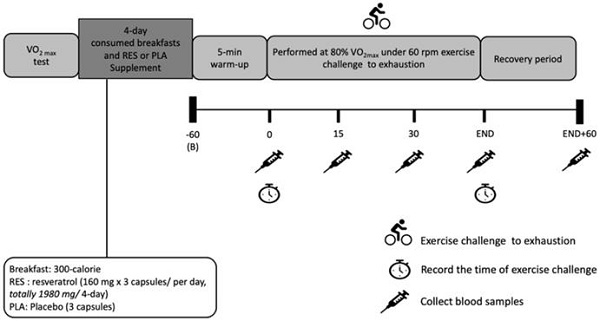
Previous studies demonstrated that resveratrol (RES) is able to enhance antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and insulin actions in humans. It is unclear whether RES can be used as ergogenic aids to enhance high-intensity cycling exercise performance and attenuate the high-intensity exercise-induced oxidative stress and inflammation. This study investigated the effect of RES supplementation on oxidative stress, inflammation, exercise-induced fatigue, and endurance performance. Eight male athletes participated in this single-blind crossover designed study and randomly instructed to receive four days of either oral RES (480 mg per day, totally 1920mg) or placebo supplementation. The cycling exercise challenge at 80% maximal oxygen consumption with 60 rpm was performed following 4 days of either RES or placebo supplementation. The total cycling performance time was recorded. In addition, blood samples were obtained to analyze the changes in blood glucose, plasma non-esterified fatty acid, serum lactate dehydrogenase, creatine kinase, uric acid, total antioxidant capacity, malondialdehyde, tumor necrosis factor-α, and interleukin-6. The exhausting time of cycling exercise challenge was not significantly increased in RES compared to that in placebo. However, IL-6 response was significantly decreased during exercise challenge in RES trial, and there were no differences in blood biomarkers, fatigue factors, and antioxidative response. Oral RES supplementation can attenuate exercise-induced IL-6 response but not fatigue and oxidative stress, inflammation response. However, we infer that 4-day oral RES supplementation has no ergogenic property on enhancing the high-intensity cycling exercise performance.
Keywords: antioxidant phytochemicals, ergogenic property, cycling exercise, fatigue

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact