3.2
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-1907
Int J Med Sci 2021; 18(9):2076-2085. doi:10.7150/ijms.54508 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Elevated plasma fatty acid-binding protein 3 is related to prolonged corrected QT interval and reduced ejection fraction in patients with stable angina
1. Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, E-Da Hospital, Kaohsiung, 82445 Taiwan.
2. Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, E-Da Hospital, Kaohsiung, 82445 Taiwan.
3. Division of General Surgery, Department of Surgery, E-Da Hospital, Kaohsiung, 82445 Taiwan.
4. Department of Emergency, E-Da Hospital, Kaohsiung, 82445 Taiwan.
5. Lee's Endocrinology Clinic, Pingtung, 90000 Taiwan.
6. School of Medicine, College of Medicine, I-Shou University, Kaohsiung, 82445 Taiwan.
7. The School of Chinese Medicine for Post Baccalaureate, College of Medicine, I-Shou University, Kaohsiung, 82445 Taiwan.
8. School of Medicine for International Students, College of Medicine, I-Shou University, Kaohsiung, 82445 Taiwan.
9. Department of Biomedical Engineering, I-Shou University, Kaohsiung, 82445 Taiwan.
10. Department of Electrical Engineering, I-Shou University, Kaohsiung, 82445 Taiwan.
11. Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, E-Da Cancer Hospital, Kaohsiung 82445 Taiwan.
12. Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, E-Da Dachang Hospital, Kaohsiung, Taiwan.
Abstract
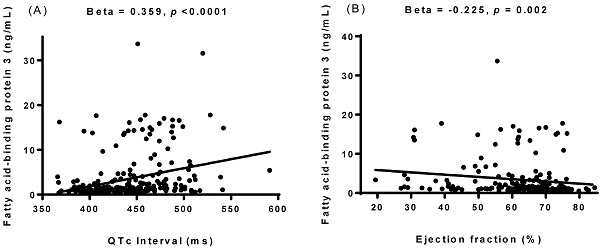
Background: Higher concentrations of plasma fatty acid-binding protein 3 (FABP3) play a role in the development of cardiovascular events, cerebrovascular deaths, and acute heart failure. However, little is known about the relationship between plasma FABP3 level and prolonged QT interval and reduced ejection fraction (EF). This study aimed to investigate the relationship between plasma FABP3 level and prolonged corrected QT (QTc) interval and reduced EF in patients with stable angina. Inflammatory cytokine and adipocytokine levels were also measured to investigate their associations with plasma FABP3.
Methods: We evaluated 249 consecutive patients with stable angina. Circulating levels of FABP3 were measured by ELISA. In addition, 12-lead ECG and echocardiography recordings were obtained from each patient.
Results: Multiple regression analysis showed that high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, high sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP), white blood cell (WBC) count, visfatin, adiponectin, FABP4, heart rate, QTc interval, left atrial diameter, left ventricular mass index, end-systolic volume, end-systolic volume index, fractional shortening, and EF were independently associated with FABP3 (all p<0.05). Patients with an abnormal QTc interval had a higher median plasma FABP3 level than those with a borderline and normal QTc interval. With increasing FABP3 tertiles, the patients had higher frequencies of abnormal QTc interval, left ventricular systolic dysfunction, and all-cause mortality, incrementally lower EF, higher WBC count, and higher levels of hs-CRP, visfatin, adiponectin, and FABP4.
Conclusion: This study indicates that plasma FABP3 may act as a surrogate parameter of prolonged QTc interval and reduced EF in patients with stable angina, partially through the effects of inflammation or cardiomyocyte injury. Further studies are required to elucidate whether plasma FABP3 plays a role in the pathogenesis of QTc prolongation and reduced EF.
Keywords: fatty acid-binding protein 3, corrected QT Interval, ejection fraction, inflammation, stable angina

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact